Lately, more often say that robots can be dangerous to humans. Many famous scientists believe that, over time, artificial intelligence will surpass their creators. Then events may begin to develop about the same as in Hollywood blockbusters in the genre of science fiction. However, any invention can be used with advantage, including intelligent robots.
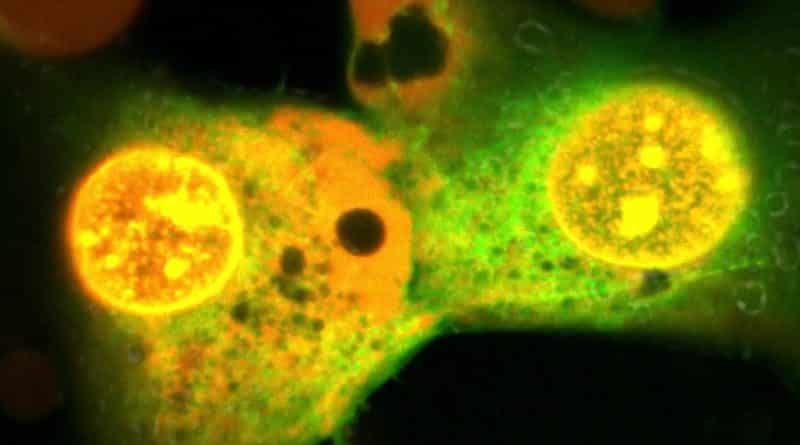
Scientists were able to create nanorobots that are able to penetrate cancer cells and destroy them in seconds. Tiny rotating moleculesin response to light, moving so fast that penetrate the membrane of the cell destroying disease. The experiments showed that the nanobots must be from 1 to 3 minutes to get through the outer membrane of prostate cancer cells.
Scientists have created several types of motor molecules, which are designed for the destruction of specific cancer cells. «Engine» tiny robots performs a chain of atoms, which, in reaction to the ultraviolet radiation causes molecules to rotate at the speed of 3 million times per second. This rotation provides the robot the power needed in order to get into a cancer cell, or to deliver to a medicine, or destroy the membrane of the tumor. It is noted that the search for the purposes of nanobots carried out without the participation of light, but to get into the cage without light they can’t.
Members of the international research team working on the project, say the robots are so small that even 50 thousand such cars a width not exceeding the diameter of a human hair.
Scientists have tested robots for the micro-organisms and small fish, plans to start testing on rodents. Only after this step succeeds, they can move on to experiments on humans.
Such an unusual way can be used in cases when chemotherapy is powerless, for example, to combat tumors in breast cancer or melanoma with skin cancer. Once the technology is perfected, it will be a real breakthrough in non-invasive cancer treatmentthat will help many people to overcome the disease.